Stylistic variants edit
The following table displays typographic and chirographic variants of each letter. For the five letters that have a different final form used at the end of words, the final forms are displayed beneath the regular form.
The block (square, or "print" type) and cursive ("handwritten" type) are the only variants in widespread contemporary use. Rashi is also used, for historical reasons, in a handful of standard texts.
| Letter name (Unicode) | Variants | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Contemporary | Early modern | Ancestral | Older Greek | |||||||||||||
| Block serif | Block sans-serif | Cursive | Rashi | Phoenician | Paleo-Hebrew | Aramaic | Greek | Orkhon | ||||||||
| Alef | א | א | 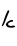 |  | 𐤀 |  | 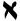 | Α | 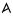 | 𐰁 𐰂 | ||||||
| Bet | ב | ב |  |  | 𐤁 | 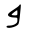 | 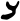 | Β |  | 𐰌 | 𐰉 | |||||
| Gimel | ג | ג |  |  | 𐤂 |  |  | Γ |  | 𐰏 | 𐰍 | 𐰐 | ||||
| Dalet | ד | ד |  |  | 𐤃 |  | 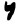 | Δ | 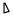 | 𐰓 | 𐰑 | 𐰖 - ДЖ | 𐰘 - дж | |||
| He | ה | ה |  |  | 𐤄 | 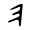 |  | Ε |  | 𐰅 | ||||||
| Vav (Unicode)[1] / Waw | ו | ו |  |  | 𐤅 |  | 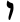 | Ϝ |  | |||||||
| Zayin | ז | ז |  |  | 𐤆 |  |  | Ζ | 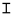 | 𐰔 | ||||||
| Chet | ח | ח |  |  | 𐤇 |  |  | Η |  | |||||||
| Tet | ט | ט |  |  | 𐤈 |  | 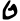 | Θ |  | |||||||
| Yod | י | י |  |  | 𐤉 | 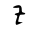 |  | Ι | 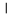 | 𐰄 | ||||||
| Kaf | כ | כ |  |  | 𐤊 |  | 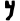 | Κ |  | 𐰚 | 𐰴 | 𐰸 | 𐰝 | 𐰜 | ||
| Final Kaf | ך | ך |  |  | ||||||||||||
| Lamed | ל | ל |  | 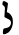 | 𐤋 |  |  | Λ | 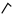 | 𐰞 | 𐰠 | |||||
| Mem | מ | מ |  |  | 𐤌 |  | 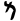 | Μ | 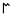 | 𐰢 | ||||||
| Final Mem | ם | ם |  |  | ||||||||||||
| Nun | נ | נ |  |  | 𐤍 |  |  | Ν |  | 𐰣 | 𐰤 | 𐰭 | ||||
| Final Nun | ן | ן |  |  | ||||||||||||
| Samekh | ס | ס |  |  | 𐤎 |  |  | Ξ | 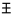 | |||||||
| Ayin | ע | ע |  | 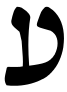 | 𐤏 |  |  | Ο | 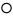 | 𐰆 | ||||||
| Pe | פ | פ |  |  | 𐤐 | 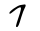 |  | Π |  | 𐰯 | ||||||
| Final Pe | ף | ף |  |  | ||||||||||||
| Tsadi | צ | צ |  |  | 𐤑 |  | 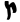 , ,  | Ϻ | 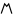 | |||||||
| Final Tsadi | ץ | ץ |  |  | ||||||||||||
| Qof | ק | ק |  |  | 𐤒 | 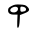 |  | Ϙ |  | |||||||
| Resh | ר | ר |  |  | 𐤓 |  | 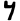 | Ρ |  | 𐰺 | 𐰼 | |||||
| Shin | ש | ש |  |  | 𐤔 |  |  | Σ |  | 𐰔 | ||||||
| Tav | ת | ת |  |  | 𐤕 |  |  | Τ |  | 𐱃 | 𐱅 | |||||
| Υ |  | 𐰈 | ||||||||||||||
| Φ |  | |||||||||||||||
| Χ | 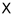 | |||||||||||||||
| Ψ | 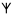 | |||||||||||||||
| Ω |  | |||||||||||||||
Yiddish symbols edit
| Symbol | Explanation |
|---|---|
| {{{1}}} | These are intended for Yiddish. They are not used in Hebrew, aside from in loan words[d]. |
| {{{1}}} | The rafe (רפה) diacritic is no longer regularly used in Hebrew. In Masoretic Texts and some other older texts, lenited consonants and sometimes matres lectionis are indicated by a small line on top of the letter. Its use has been largely discontinued in modern printed texts. It is still used to mark fricative consonants in the YIVO orthography of Yiddish. |
🔥 Top keywords: Akademia e Shkencave e RPS te ShqiperiseAlexandria Ocasio-CortezBilderberg GroupCristiano RonaldoDong XiaowanMinecraftOperation GladioPrimal cutRiot FestStrictly Come Dancing (series 7)Main PageSpecial:SearchDonald TrumpWikipedia:Featured picturesLuka DončićCleopatraProsecution of Donald Trump in New YorkDeaths in 2024Kyrie IrvingStormy DanielsDrew Gordon2024 South African general electionYouTube2024 Indian general electionJuan MerchanFuriosa: A Mad Max SagaProject 2025EminemInughuit2024 ICC Men's T20 World CupKepler's Supernova.xxxMichael FinleyStormy Daniels–Donald Trump scandalJason KiddDallas MavericksEric (miniseries)Neatsville, KentuckyThe First OmenCivil War (film)Todd BlancheAlesha DixonPortal:Current eventsXXX (2002 film)Michael Cohen (lawyer)List of digital camera brandsBiggest ball of twine2024 United States presidential electionList of NBA champions