In the United States Navy, officers have various ranks. Equivalency between services is by pay grade. United States Navy commissioned officer ranks have two distinct sets of rank insignia: On dress uniform a series of stripes similar to Commonwealth naval ranks are worn; on service khaki, working uniforms (Navy Working Uniform [NWU], and coveralls), and special uniform situations (combat utilities, flight suits, and USMC uniforms when worn by Navy officers assigned or attached to USMC units), the rank insignia are identical to the equivalent rank in the US Marine Corps.
Commissioned officer ranks edit
| US DoD pay grade | Special grade[a] | O-10 | O-9 | O-8 | O-7 | O-6 | O-5 | O-4 | O-3 | O-2 | O-1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NATO code | OF-10 | OF-9 | OF-8 | OF-7 | OF-6 | OF-5 | OF-4 | OF-3 | OF-2 | OF-1 | |
| Insignia |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| Uniform insignia |   |   |   |   |   |   |   |   |   |   |   |
| Title | Fleet admiral | Admiral | Vice admiral | Rear admiral | Rear admiral (lower half) | Captain | Commander | Lieutenant commander | Lieutenant | Lieutenant (junior grade) | Ensign |
| Abbreviation | FADM | ADM | VADM | RADM | RDML | CAPT | CDR | LCDR | LT | LTJG | ENS |
Warrant officer ranks edit
| US DoD pay grade | W-5 | W-4 | W-3 | W-2 | W-1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NATO code | WO-5 | WO-4 | WO-3 | WO-2 | WO-1 |
| Insignia |  |  |  |  |  |
| Title | Chief warrant officer 5 | Chief warrant officer 4 | Chief warrant officer 3 | Chief warrant officer 2 | Warrant officer 1 |
| Abbreviation | CWO-5 | CWO-4 | CWO-3 | CWO-2 | WO-1 |
Rank categories edit
In the U.S. Navy, pay grades for officers are:
- W-1 for warrant officer one. Warrant officers appointed to this grade are normally done via a warrant from the Secretary of the Navy.[1]
- W-2 to W-5 for chief warrant officers. Chief warrant officers (CWO2 to CWO5) are appointed via commission.[1]
- O-1 to O-10. Officers appointed to these grades are done via commission.[2]
- O-1 through O-4 are junior officers: ensign, lieutenant (junior grade), lieutenant, and lieutenant commander.
- O-5 and O-6 are senior officers: commander and captain.
- O-7 through O-10 are flag officers: rear admiral (lower half) (one star), rear admiral (two stars), vice admiral (three stars), and admiral (four stars).[3][4]
- Fleet admiral was a five-star flag officer rank. It was awarded to four officers during World War II and has not been authorized since. However, the rank of fleet admiral still remains listed on official rank insignia precedence charts and, if needed, this rank could be reestablished at the discretion of Congress and the President. All five-star officers are, technically, unable to retire from active duty.[5] The last living fleet admiral, Chester W. Nimitz, died in 1966.
Rank and promotion system edit
If an officer demonstrates superior performance and proves themselves capable of performing at the next higher pay grade, then they are given an increase in pay grade. The official term for this process is a promotion.
Commissioned naval officers originate from the United States Naval Academy, the United States Merchant Marine Academy, other Service Academies (United States Military Academy, United States Coast Guard Academy, or United States Air Force Academy), Naval Reserve Officer Training Corps (NROTC), Officer Candidate School (OCS), the since-disestablished Aviation Officer Candidate School (AOCS), and a host of other commissioning programs such as the "Seaman to Admiral-21" program and the limited duty officer/chief warrant officer (LDO/CWO) selection program. There are also a small number of direct commissioned officers, primarily staff corps officers in the medical, dental, nurse, chaplain and judge advocate general career fields.
Commissioned officers can generally be divided into line officers and staff corps:
- Line officers (or officers of the line) derive their name from the 18th-century tactic of employing warships in a line of battle to take advantage of cannon on each side of the ship. These vessels were dubbed ships of the line and those who commanded them were likewise called "line officers." Today, all United States Navy unrestricted line and restricted line officers denote their status with a star located above their rank insignia on the sleeves of their dress blue uniforms and shoulder boards of their white uniforms; metal rank insignia devices on both collar-points of khaki shirts/blouses; and cloth equivalents on both collar-points of blue NWUs. Officers of the staff corps replace the star (or the left collar-point on applicable shirts/blouses) with different insignias to indicate their field of specialty.[6] Line officers can be categorized into unrestricted and restricted communities.
- Unrestricted line officers (URL) are the most visible and well-known of line officers, due to their role as the Navy's war-fighting command element. They receive training in weapons systems, tactics, strategy, command and control, and are considered unrestricted because they are authorized to command combatant ships, combat aviation squadrons/air groups/air wings, and special operations units at sea, or combat aviation squadrons/air groups/air wings or special operations units deployed ashore. URL officers are naval aviators (and Naval Aviator-Astronauts), Naval Flight Officers (and Naval Flight Officer-Astronauts), Surface Warfare Officers, Submarine Warfare Officers, Special Warfare Officers (e.g., Sea-Air-Land, or SEAL Officers), and Special Operations/Explosive Ordnance Disposal (EOD) Officers.
- Restricted line officers (RL) concentrate on non-combat related fields, which include marine engineering, aeronautical engineering, ship maintenance, aircraft maintenance, meteorology and oceanography, naval intelligence, information technology, manpower/human resources, public affairs, and a host of other career fields. They are not qualified to command combat units, but can command organizations in their respective specialized career fields. In certain shipboard environments, many unrestricted line officers fill what might be considered restricted line duties, such as the officers in a ship's or submarine's engineering department. Because they maintain their general surface warfare or submarine warfare specialist duties instead of completely specializing in one career area, they maintain their unrestricted line command career path.
- Staff corps officers are specialists in fields that are themselves professional careers and not exclusive to the military, for example health care, law, civil engineering and religion. There are eight staff corps: Medical Corps, Dental Corps, Nurse Corps, Medical Service Corps, Chaplain Corps, Navy Supply Corps, Judge Advocate General's Corps, and Civil Engineer Corps. They primarily exist to augment the line communities and are able to be assigned to both line and staff commands. One exception to this is the case of Civil Engineer Corps officers, who serve as both the Public Works Officers and Resident Officers in Charge of Construction (ROICC) at naval shore installations, and as officers for Construction Battalion (Seabee) units. This latter role requires them to serve in a command capacity for ground combatants when the Seabees are deployed to combat areas.
Note 2: See also Commodore (United States) — today an honorific title (but not a pay grade) for selected URL captains (O-6) in major command of multiple subordinate operational units, and formerly a rank (O-7).[7]
Note 3: The term "line officer of the naval service" includes line officers of both the Navy and the Marine Corps. All U.S. Marine Corps officers are considered "of the line," including Marine Corps limited duty officers, chief warrant officers, and warrant officers, regardless of grade or specialty.[8]
"Tombstone promotions" edit
The Act of Congress of March 4, 1925, provided for Navy, Marine Corps, and Coast Guard officers to be promoted one grade upon retirement, if they had been specially commended for performance of duty in actual combat, known as "tombstone promotions". Officers who received such tombstone promotions, or also known as "tombstone officer", carried the loftier title but did not draw the additional retirement pay of their higher rank. The Act of Congress of February 23, 1942, enabled promotions to three- and four-star grades. Promotions were subsequently restricted to citations issued before January 1, 1947, and finally eliminated altogether effective November 1, 1959.[9]
Any officer who served honorably in a grade while on active duty receives precedence on the retirement list over any "tombstone officers" of the same grade, while "tombstone officers" of the same grade rank among each other according to their dates of rank in their highest active duty grade.[10]
Officer designator devices edit
The Navy uses the term designator, instead of the term military occupational specialty (MOS) or Air Force Specialty Code (AFSC), to determine an officer's job specialty. Navy officers are designated as either as a line officer or as a staff corps officer. Unrestricted line (URL) and restricted line (RL) officers wear an embroidered gold star above their rank of the naval service dress uniform and, if they are in a rank below rear admiral (lower half), their shoulder board insignia, while staff corps officers and chief warrant officers wear unique designator devices.[11][12]
| Type | Line officer | Medical Corps | Dental Corps | Nurse Corps | Medical Service Corps | Judge Advocate General's Corps |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Insignia |  |  |  |  |  | 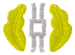 |
| Designator1 | 1XXX | 210X | 220X | 290X | 230X | 250X |
| Chaplain Corps (Christian Faith) | Chaplain Corps (Jewish Faith) | Chaplain Corps (Muslim Faith) | Chaplain Corps (Buddhist Faith) | Supply Corps | Civil Engineer Corps | Law Community (Limited Duty Officer) |
 |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| 410X | 410X | 410X | 410X | 310X | 510X | 655X |
 1 An officer designator describes their general community or profession. The final (fourth) digit (X) denotes whether the officer has a regular (0), reserve (5), or full-time support (7) commission.[13] | ||||||
The chief warrant officer and staff corps devices are also worn on the left collar of uniforms.
Timeline of changes edit
This table shows changes in insignia based on the date they appeared in or were removed from uniform regulations or official orders.[14]
| US DoD Pay Grade | Special Grade | O-10 | O-9 | O-8 | O-7 | O-6 | O-5 | O-4 | O-3 | O-2 | O-1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Admiral of the Navy and Fleet Admiral | Admiral | Vice admiral | Rear admiral | Commodore | Captain | Commander | Lieutenant commander | Lieutenant | Lieutenant (junior grade) | Ensign |
 (March 1852) | No equivalent |  |  |  | No equivalent |  |  | No equivalent | |||
 (July 1862) | No equivalent |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  | ||
 (May 1863) | No equivalent |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  | ||
 (Jan. 1864) | No equivalent |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  | ||
 (Jan. 1865) | No equivalent |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  | |
 (Dec. 1866) | No equivalent |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |
 (March 1869) | No equivalent |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |
 (May 1869) | No equivalent |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |
 (Nov. 1874) | No equivalent |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |
 (Aug. 1881) | No equivalent |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |
 (July 1897) | No equivalent |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  | ||
 (May 1899) | No equivalent |  | No equivalent |  | No equivalent |  |  |  |  |  |  |
 (Jan. 1905) | 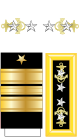 | No equivalent |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  | |
 (Jan. 1913) |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |
 (Sept. 1922) | No equivalent |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |
 (Jan. 1945) |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| Title | Admiral of the Navy and Fleet Admiral | Admiral | Vice admiral | Rear admiral | Commodore | Captain | Commander | Lieutenant commander | Lieutenant | Lieutenant (junior grade) | Ensign |
| NATO Code | OF-10 | OF-9 | OF-8 | OF-7 | OF-6 | OF-5 | OF-4 | OF-3 | OF-2 | OF-1 | |
See also edit
- Badges of the United States Navy
- List of United States Naval officer designators
- United States Navy staff corps
- Naval officer ranks — comparison to other countries and explanation of NATO rank codes
- Navy Enlisted Classification
- Scrambled egg (uniform) shows differences in hats
- Staff (military)
- Uniforms of the United States Navy
- U.S. Navy midshipman rank insignia can be found in the Midshipman article.
- U.S. Navy warrant officer rank insignia can be found in the Warrant officer (United States) article.
- List of United States Navy enlisted rates
Notes edit
- ^ Reserved for wartime use only.
References edit
External links edit
- "Officer Rank Insignia". Bureau of Personnel Uniform Regulations. U.S. Navy. Chapter 4, Section 1. Archived from the original on 2 February 2007.
- "Officers Rank". Rank Insignias. U.S. Department of Defense.
- "Office of Information". U.S. Navy. Archived from the original on 13 September 2008.
- "Official list of United States military rank insignia". defenselink.mil.
