Saisiyat (sometimes spelled Saisiat) is the language of the Saisiyat, a Taiwanese indigenous people. It is a Formosan language of the Austronesian family. It has approximately 4,750 speakers.
| Saisiyat | |
|---|---|
| SaiSiyat | |
| Native to | Taiwan |
| Ethnicity | 7,900 |
Native speakers | 4,750 (2002)[1] |
Austronesian
| |
| Dialects |
|
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | xsy |
| Glottolog | sais1237 |
| ELP | Saisiyat |
 | |
Distribution edit
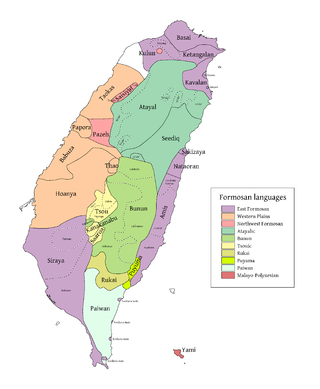
The language area of Saisiyat is small, situated in the northwest of the country between the Hakka Chinese and Atayal regions in the mountains (Wufeng, Hsinchu; Nanchuang and Shitan, Miaoli).
There are two main dialects: Ta'ai (North Saisiyat) and Tungho (South Saisiyat). Ta'ai is spoken in Hsinchu and Tungho is spoken in Miao-Li.
Kulon, an extinct Formosan language, is closely related to Saisiyat but is considered by Taiwanese linguist Paul Jen-kuei Li to be a separate language.
Usage edit
Today, one thousand Saisiyat people do not use the Saisiyat language. Many young people use Hakka or Atayal instead, and few children speak Saisiyat. Hakka Chinese speakers, Atayal speakers and Saisiyat speakers live more or less together. Many Saisiyat are able to speak Saisiyat, Hakka, Atayal, Mandarin, and, sometimes, Min Nan as well. Although Saisiyat has a relatively large number of speakers, the language is endangered.
Orthography edit
- a - [ä]
- ae - [æ]
- b - [β]
- e - [ə]
- ng - [ŋ]
- oe - [œ]
- s - [s/θ]
- S - [ʃ]
- y - [j]
- z - [z/ð]
- ' - [ʔ]
- aa/aː - [aː]
- ee/eː - [əː]
- ii/iː - [iː][3]
Phonology edit
Consonants edit
| Labial | Alveolar | Post-alveolar | Dorsal | Glottal | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nasal | m | n | ŋ | |||||||
| Plosive | p | t | k | ʔ | ||||||
| Fricative | s | z | ʃ | h | ||||||
| Approximant | w | l | ɭ | j | ||||||
| Trill | r | |||||||||
Orthographic notes:
- /ɭ/ is a retroflex lateral approximant, while /ʃ/ is a palato-alveolar fricative.[4]
Vowels edit
| Front | Central | Back | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Close | i | ||
| Close-mid | o | ||
| Mid | ə | ||
| Open-mid | œ | ||
| Open | æ | ä |
Grammar edit
Syntax edit
Although it also allows for verb-initial constructions,[5] Saisiyat is a strongly subject-initial language (i.e., SVO), and is shifting to an accusative language, while it still has many features of split ergativity (Hsieh & Huang 2006:91). Pazeh and Thao, also Northern Formosan languages, are the only other Formosan languages that allow for SVO constructions.
Saisiyat's case-marking system distinguishes between personal and common nouns (Hsieh & Huang 2006:93).
| Type of Noun | Nominative | Accusative | Genitive | Dative | Possessive | Locative |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Personal | Ø, hi | hi | ni | 'an-a | 'ini' | kan, kala |
| Common | Ø, ka | ka | noka | 'an noka-a | no | ray |
Pronouns edit
Saisiyat has an elaborate pronominal system (Hsieh & Huang 2006:93).
| Type of Pronoun | Nominative | Accusative | Genitive | Dative | Possessive | Locative |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1s. | yako/yao | yakin/'iyakin | ma'an | 'iniman | 'amana'a | kanman |
| 2s. | So'o | 'iso'on | niSo | 'iniSo | 'anso'o'a | kanSo |
| 3s. | sia | hisia | nisia | 'inisia | 'ansiaa | kansia |
| 1p. (incl.) | 'ita | 'inimita | mita' | 'inimita' | 'anmita'a | kan'ita |
| 1p. (excl.) | yami | 'iniya'om | niya'om | 'iniya'om | 'anya'oma | kanyami |
| 2p. | moyo | 'inimon | nimon | 'inimon | 'anmoyoa | kanmoyo |
| 3p. | lasia | hilasia | nasia | 'inilasia | 'anlasiaa | kanlasia |
Verbs edit
The following are verbal prefixes in Saisiyat (Hsieh & Huang 2006:93).
| Type of Focus | I | II |
|---|---|---|
| Agent Focus (AF) | m-, -om-, ma-, Ø | Ø |
| Patient Focus (PF) | -en | -i |
| Locative Focus (LF) | -an | — |
| Referential Focus (RF) | si-, sik- | -ani |
Saisiyat verbs can be nominalized in the following ways.[6]
| Lexical nominalization | Syntactic nominalization | Temporal/Aspectual | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Agent | ka-ma-V | ka-pa-V | Habitual, Future |
| Patient | ka-V-en, V-in- | ka-V-en, V-in- | Future (for ka-V-en), Perfective (for V-in-) |
| Location | ka-V-an | ka-V-an | Future |
| Instrument | ka-V, Ca-V (reduplication) | ka-V, Ca-V (reduplication) | Future |
References edit
Citations edit
- ^ Saisiyat at Ethnologue (19th ed., 2016)

- ^ "Táiwān yuánzhùmín píngpǔ zúqún bǎinián fēnlèi shǐ xìliè dìtú" 臺灣原住民平埔族群百年分類史系列地圖 [A History of the Classification of Plains Taiwanese Tribes Over the Past Century]. blog.xuite.net (in Chinese). 2009-08-06. Retrieved 2017-03-04.
- ^ "Saisiyat (SaySiyat)". Omniglot.
- ^ Jiang, Wenyu; I, Chang-Liao; Chiang, Fang-Mei (2006). "The Prosodic Realization of Negation in Saisiyat and English" (PDF). Oceanic Linguistics. 45 (1): 110–132. doi:10.1353/ol.2006.0007. JSTOR 4499949. S2CID 144937416.
- ^ Li, Paul Jen-kuei (2004) [1998]. 台灣南島語言 [The Austronesian Languages of Taiwan]. In Li, Paul Jen-kuei (ed.). Selected Papers on Formosan Languages. Taipei, Taiwan: Institute of Linguistics, Academia Sinica.
- ^ Yeh, Marie Mei-li (n.d.), Nominalization in Saisiyat, Hsinchu, Taiwan: National Hsinchu University of Education
Works cited edit
- Hsieh, Fuhui; Huang, Xuanfan (2006). "The Pragmatics of Case Marking in Saisiyat". Oceanic Linguistics. 45 (1): 91–109. doi:10.1353/ol.2006.0012. S2CID 145322522.
- Li, Paul Jen-kuei (1978). "A Comparative Vocabulary of Saisiyat Dialects" (PDF). Bulletin of the Institute of History and Philology. 49. Academia Sinica: 133–199.
Further reading edit
- Yeh, Mei-li 葉美利 (2018). Sàixiàyǔ yǔfǎ gàilùn 賽夏語語法概論 [Introduction to Saisiyat Grammar] (in Chinese). Xinbei Shi: Yuanzhu minzu weiyuanhui. ISBN 978-986-05-5684-1 – via alilin.apc.gov.tw.
- Zeitoun, Elizabeth; Chu, Tai-hwa; Lalo a tahesh Kaybaybaw (2015). A Study of Saisiyat Morphology. Honolulu: University of Hawaiʻi Press. ISBN 978-0-8248-5042-5.
External links edit
- Yuánzhùmínzú yǔyán xiànshàng cídiǎn 原住民族語言線上詞典 (in Chinese) – Saisiyat search page at the "Aboriginal language online dictionary" website of the Indigenous Languages Research and Development Foundation
- Saisiyat teaching and leaning materials published by the Council of Indigenous Peoples of Taiwan (in Chinese)
- Saisiyat translation of President Tsai Ing-wen's 2016 apology to indigenous people – published on the website of the presidential office

