Capillary action (sometimes called capillarity, capillary motion, capillary rise, capillary effect, or wicking) is the process of a liquid flowing in a narrow space in opposition to or at least without the assistance of any external forces like gravity.

The effect can be seen in the drawing up of liquids between the hairs of a paint-brush, in a thin tube such as a straw, in porous materials such as paper and plaster, in some non-porous materials such as clay and liquefied carbon fiber, or in a biological cell.
It occurs because of intermolecular forces between the liquid and surrounding solid surfaces. If the diameter of the tube is sufficiently small, then the combination of surface tension (which is caused by cohesion within the liquid) and adhesive forces between the liquid and container wall act to propel the liquid.
Etymology
editCapillary comes from the Latin word capillaris, meaning "of or resembling hair". The meaning stems from the tiny, hairlike diameter of a capillary.
History
editThe first recorded observation of capillary action was by Leonardo da Vinci.[1][2] A former student of Galileo, Niccolò Aggiunti, was said to have investigated capillary action.[3] In 1660, capillary action was still a novelty to the Irish chemist Robert Boyle, when he reported that "some inquisitive French Men" had observed that when a capillary tube was dipped into water, the water would ascend to "some height in the Pipe". Boyle then reported an experiment in which he dipped a capillary tube into red wine and then subjected the tube to a partial vacuum. He found that the vacuum had no observable influence on the height of the liquid in the capillary, so the behavior of liquids in capillary tubes was due to some phenomenon different from that which governed mercury barometers.[4]
Others soon followed Boyle's lead.[5] Some (e.g., Honoré Fabri,[6] Jacob Bernoulli[7]) thought that liquids rose in capillaries because air could not enter capillaries as easily as liquids, so the air pressure was lower inside capillaries. Others (e.g., Isaac Vossius,[8] Giovanni Alfonso Borelli,[9] Louis Carré,[10] Francis Hauksbee,[11] Josia Weitbrecht[12]) thought that the particles of liquid were attracted to each other and to the walls of the capillary.
Although experimental studies continued during the 18th century,[13] a successful quantitative treatment of capillary action[14] was not attained until 1805 by two investigators: Thomas Young of the United Kingdom[15] and Pierre-Simon Laplace of France.[16] They derived the Young–Laplace equation of capillary action. By 1830, the German mathematician Carl Friedrich Gauss had determined the boundary conditions governing capillary action (i.e., the conditions at the liquid-solid interface).[17] In 1871, the British physicist Sir William Thomson (later Lord Kelvin) determined the effect of the meniscus on a liquid's vapor pressure—a relation known as the Kelvin equation.[18] German physicist Franz Ernst Neumann (1798–1895) subsequently determined the interaction between two immiscible liquids.[19]
Albert Einstein's first paper, which was submitted to Annalen der Physik in 1900, was on capillarity.[20][21]
Phenomena and physics
edit

Capillary penetration in porous media shares its dynamic mechanism with flow in hollow tubes, as both processes are resisted by viscous forces.[22] Consequently, a common apparatus used to demonstrate the phenomenon is the capillary tube. When the lower end of a glass tube is placed in a liquid, such as water, a concave meniscus forms. Adhesion occurs between the fluid and the solid inner wall pulling the liquid column along until there is a sufficient mass of liquid for gravitational forces to overcome these intermolecular forces. The contact length (around the edge) between the top of the liquid column and the tube is proportional to the radius of the tube, while the weight of the liquid column is proportional to the square of the tube's radius. So, a narrow tube will draw a liquid column along further than a wider tube will, given that the inner water molecules cohere sufficiently to the outer ones.
Examples
editIn the built environment, evaporation limited capillary penetration is responsible for the phenomenon of rising damp in concrete and masonry, while in industry and diagnostic medicine this phenomenon is increasingly being harnessed in the field of paper-based microfluidics.[22]
In physiology, capillary action is essential for the drainage of continuously produced tear fluid from the eye. Two canaliculi of tiny diameter are present in the inner corner of the eyelid, also called the lacrimal ducts; their openings can be seen with the naked eye within the lacrymal sacs when the eyelids are everted.
Wicking is the absorption of a liquid by a material in the manner of a candle wick.
Paper towels absorb liquid through capillary action, allowing a fluid to be transferred from a surface to the towel. The small pores of a sponge act as small capillaries, causing it to absorb a large amount of fluid. Some textile fabrics are said to use capillary action to "wick" sweat away from the skin. These are often referred to as wicking fabrics, after the capillary properties of candle and lamp wicks.
Capillary action is observed in thin layer chromatography, in which a solvent moves vertically up a plate via capillary action. In this case the pores are gaps between very small particles.
Capillary action draws ink to the tips of fountain pen nibs from a reservoir or cartridge inside the pen.
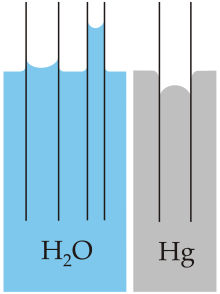
With some pairs of materials, such as mercury and glass, the intermolecular forces within the liquid exceed those between the solid and the liquid, so a convex meniscus forms and capillary action works in reverse.
In hydrology, capillary action describes the attraction of water molecules to soil particles. Capillary action is responsible for moving groundwater from wet areas of the soil to dry areas. Differences in soil potential (
A practical application of capillary action is the capillary action siphon. Instead of utilizing a hollow tube (as in most siphons), this device consists of a length of cord made of a fibrous material (cotton cord or string works well). After saturating the cord with water, one (weighted) end is placed in a reservoir full of water, and the other end placed in a receiving vessel. The reservoir must be higher than the receiving vessel.[23] A related but simplified capillary siphon only consists of two hook-shaped stainless-steel rods, whose surface is hydrophilic, allowing water to wet the narrow grooves between them.[24] Due to capillary action and gravity, water will slowly transfer from the reservoir to the receiving vessel. This simple device can be used to water houseplants when nobody is home. This property is also made use of in the lubrication of steam locomotives: wicks of worsted wool are used to draw oil from reservoirs into delivery pipes leading to the bearings.[25]
In plants and animals
editCapillary action is seen in many plants, and plays a part in transpiration. Water is brought high up in trees by branching; evaporation at the leaves creating depressurization; probably by osmotic pressure added at the roots; and possibly at other locations inside the plant, especially when gathering humidity with air roots.[26][27][28]
Capillary action for uptake of water has been described in some small animals, such as Ligia exotica[29] and Moloch horridus.[30]
Height of a meniscus
editCapillary rise of liquid in a capillary
edit
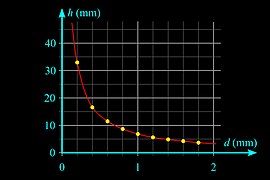
The height h of a liquid column is given by Jurin's law[31]
where 
As r is in the denominator, the thinner the space in which the liquid can travel, the further up it goes. Likewise, lighter liquid and lower gravity increase the height of the column.
For a water-filled glass tube in air at standard laboratory conditions, γ = 0.0728 N/m at 20 °C, ρ = 1000 kg/m3, and g = 9.81 m/s2. Because water spreads on clean glass, the effective equilibrium contact angle is approximately zero.[33] For these values, the height of the water column is
Thus for a 2 m (6.6 ft) radius glass tube in lab conditions given above, the water would rise an unnoticeable 0.007 mm (0.00028 in). However, for a 2 cm (0.79 in) radius tube, the water would rise 0.7 mm (0.028 in), and for a 0.2 mm (0.0079 in) radius tube, the water would rise 70 mm (2.8 in).
Capillary rise of liquid between two glass plates
editThe product of layer thickness (d) and elevation height (h) is constant (d·h = constant), the two quantities are inversely proportional. The surface of the liquid between the planes is hyperbola.
- Water between two glass plates
Liquid transport in porous media
edit
When a dry porous medium is brought into contact with a liquid, it will absorb the liquid at a rate which decreases over time. When considering evaporation, liquid penetration will reach a limit dependent on parameters of temperature, humidity and permeability. This process is known as evaporation limited capillary penetration[22] and is widely observed in common situations including fluid absorption into paper and rising damp in concrete or masonry walls. For a bar shaped section of material with cross-sectional area A that is wetted on one end, the cumulative volume V of absorbed liquid after a time t is
where S is the sorptivity of the medium, in units of m·s−1/2 or mm·min−1/2. This time dependence relation is similar to Washburn's equation for the wicking in capillaries and porous media.[34] The quantity
is called the cumulative liquid intake, with the dimension of length. The wetted length of the bar, that is the distance between the wetted end of the bar and the so-called wet front, is dependent on the fraction f of the volume occupied by voids. This number f is the porosity of the medium; the wetted length is then
Some authors use the quantity S/f as the sorptivity.[35]
The above description is for the case where gravity and evaporation do not play a role.
Sorptivity is a relevant property of building materials, because it affects the amount of rising dampness. Some values for the sorptivity of building materials are in the table below.
| Material | Sorptivity (mm·min−1/2) |
|---|---|
| Aerated concrete | 0.50 |
| Gypsum plaster | 3.50 |
| Clay brick | 1.16 |
| Mortar | 0.70 |
| Concrete brick | 0.20 |
See also
edit- Bond number – Dimensionless number in fluid dynamics
- Bound water – Thin layer of water surrounding mineral surfaces.
- Capillary fringe – Subsurface layer in which groundwater seeps up from a water table by capillary action
- Capillary pressure – Pressure between two fluids from forces between the fluids and tube walls
- Capillary wave – Wave on the surface of a fluid, dominated by surface tension
- Capillary bridges – Minimised surface of liquid commecting two wetted objects
- Damp proofing – Type of moisture control in building construction
- Darcy's law – Equation describing the flow of a fluid through a porous medium
- Frost flower – Thin layer of ice extruded from a plant
- Frost heaving – Upwards swelling of soil during freezing
- Hindu milk miracle – 1995 alleged miracle incidents
- Krogh model
- Porosimetry – Measurement and characterization of the porosity of a material
- Needle ice – Ice column formed when liquid groundwater rises into freezing air
- Surface tension – Tendency of a liquid surface to shrink to reduce surface area
- Washburn's equation – Equation describing the penetration length of a liquid into a capillary tube with time
- Young–Laplace equation – Describing pressure difference over an interface in fluid mechanics
References
editFurther reading
edit
- de Gennes, Pierre-Gilles; Brochard-Wyart, Françoise; Quéré, David (2004). Capillarity and Wetting Phenomena. Springer New York. doi:10.1007/978-0-387-21656-0. ISBN 978-1-4419-1833-8.