Louis Armstrong New Orleans International Airport (IATA: MSY, ICAO: KMSY, FAA LID: MSY) is an international airport under Class B airspace in Kenner city, Jefferson Parish, Louisiana, United States. It is owned by the city of New Orleans and is 11 miles (18 km) west of downtown New Orleans.[3] A small portion of Runway 11/29 is in unincorporated St. Charles Parish. Armstrong International is the primary commercial airport for the New Orleans metropolitan area and southeast Louisiana.
Louis Armstrong New Orleans International Airport Moisant Field | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||||
 2006 USGS orthophoto, prior to the construction of the current terminal | |||||||||||||||
| Summary | |||||||||||||||
| Airport type | Public | ||||||||||||||
| Owner/Operator | New Orleans Aviation Board | ||||||||||||||
| Serves | New Orleans metropolitan area | ||||||||||||||
| Location | Kenner, Louisiana, United States | ||||||||||||||
| Operating base for | Breeze Airways | ||||||||||||||
| Elevation AMSL | 4 ft / 1 m | ||||||||||||||
| Coordinates | 29°59′36″N 090°15′29″W / 29.99333°N 90.25806°W | ||||||||||||||
| Website | flymsy.com | ||||||||||||||
| Maps | |||||||||||||||
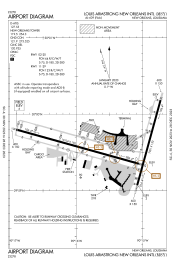 FAA airport diagram | |||||||||||||||
 | |||||||||||||||
| Runways | |||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||
| Statistics (2023) | |||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||
MSY covers 1,500 acres (607 ha) of land.[3][4] At an average of 4.5 feet (1.4 m) above sea level, MSY is the third lowest-lying international airport in the world, only behind Amsterdam Airport Schiphol in the Netherlands, which is 11 feet (3.4 m) below sea level, and Atyrau International Airport in Kazakhstan, which lies 72 feet (22 m) below sea level.
History edit

Beginnings edit
Plans for a new airport began in 1940, as evidence mounted that the older Shushan Airport (New Orleans Lakefront Airport) was too small.
The airport was originally named Moisant Field after daredevil aviator John Moisant, who died in 1910 in an airplane crash on agricultural land where the airport is now located. Its IATA code MSY was derived from Moisant Stock Yards, as Lakefront Airport retained the code NEW.[5] In World War II the land became a government air base. It returned to civil control after the war and commercial service began at Moisant Field in May 1946. In September 1947, the airport was shut down as it was submerged under two feet of water in the wake of the 1947 Fort Lauderdale Hurricane's impact.
When commercial service began at Moisant Field in 1946, the terminal was a large, makeshift hangar-like building—a sharp contrast to airports in then-peer cities. A new terminal complex debuted in 1959 towards the end of Mayor DeLesseps "Chep" Morrison's administration.[6] The core of this structure formed much of the facility used until November 2019. It is situated on the south side of the airfield. The terminal contained two sections, East and West, connected by a central ticketing alley. Four concourses, A, B, C and D, were attached to the terminal, and had a total of 47 gates. The vaulted arrivals lounge at the head of Concourse C and the adjacent, western half of the ticketing alley are the remaining portions of the airport's 1959 terminal complex.
Retired United States Air Force Major General Junius Wallace Jones served as airport director in the 1950s. During his term, the airport received many improvements. By the time the previous airport terminal building opened in 1959, the name Moisant International Airport was being used for the New Orleans facility. In 1961, the name was changed to New Orleans International Airport.[7] In the early 1970s, the airport was expanded. A lengthened main terminal ticketing area, an airport access road linking the terminal to I-10, and Concourses A and B were constructed.
In July 1978, National Airlines began service to Frankfurt via Amsterdam aboard McDonnell Douglas DC-10s. This was New Orleans' first transatlantic flight.[8][9][10] Less than a month later, National added a stop in Tampa due to low demand.[11] In May 1981, British Airways inaugurated a flight from London's Gatwick Airport to Mexico City that stopped in New Orleans. It flew a Lockheed L-1011 TriStar on the route.[12][13][14] The airline discontinued the service in October 1982 because of financial problems.[15]
Northeastern International Airways operated a small hub at MSY in the spring of 1984.[16][17] Another airline that attempted to operate a hub at MSY was short-lived Pride Air which was based in New Orleans and was operating nonstop or direct Boeing 727 service from the airport to sixteen destinations including cities in California, Florida, and the western U.S. in the summer of 1985.[18]
In July 2001, to honor the 100th anniversary of Louis Armstrong's birth (August 4, 1901), the airport's name became Louis Armstrong New Orleans International Airport.[19]
Post-Hurricane Katrina capacity restoration edit

MSY reopened to commercial flights on September 13, 2005, after the devastation of Hurricane Katrina the previous month, with four flights operated by Delta Air Lines to Atlanta and a Northwest Airlines flight to Memphis. Slowly, service from other carriers began to resume. All international service into MSY was suspended while the FIS facility was closed post-Katrina. The facility reopened to chartered flights arriving from London, Manchester, Bournemouth, and Nottingham, UK—all carrying tourists in for Mardi Gras and set to depart aboard a cruise liner.
MSY served 9,785,394 passengers in 2014, exceeding for the first time in the post-Katrina era the total passenger count of 9,733,179 achieved in 2004, the last full calendar year prior to Katrina's landfall in August 2005. A new record passenger count was set by the airport in 2015. 10,673,301 passengers were served, eclipsing the earlier record of 9.9 million passengers, set in 2000. In 2019 the airport served 13.1 million passengers.
In December 2015, the New Orleans Aviation Board, along with New Orleans Mayor Mitch Landrieu and City Council, approved a plan to build a new $598 million terminal building on the north side of the airport property with two concourses and 30 gates.[20] Designed by world-renowned Argentine-American architect Cesar Pelli, construction on the new main terminal began in January 2016. During the construction, the scope of the project was expanded so the terminal would feature 35 gates.[21] In March 2017, British Airways commenced nonstop service to London's Heathrow Airport on a Boeing 787.[22] The new terminal opened in November 2019 at a cost of $1.3 billion.[23][24]
Facilities edit
Terminal edit

MSY has a single terminal with three concourses labeled A, B, and C. There is a total of 35 gates.[25] Departures and Ticketing are on Level 3, TSA Security Screening is on Level 2, and Arrivals and Baggage Claim are on Level 1.[26] International flights are processed in Concourse A, which contains the airport's customs facilities.
Ground transportation edit
The terminal is served by Interstate 10.[27] Bus service between the airport and downtown New Orleans is provided by New Orleans Regional Transit Authority Airport Express Route 202 and Jefferson Transit bus E-2.[28] Airport Shuttle has services to most hotels and hostels in the Central Business District of New Orleans.[29] The rental car facility is on the south side of the airfield next to the former terminal.[30]
Airlines and destinations edit
Passenger edit
Cargo edit
| Airlines | Destinations |
|---|---|
| Amazon Air | Cincinnati, Lakeland |
| DHL Aviation | Cincinnati, Houston–Intercontinental, Memphis |
| FedEx Express | Indianapolis, Memphis |
| UPS Airlines | Houston–Intercontinental, Louisville |
Statistics edit
Passenger numbers edit
Graphs are unavailable due to technical issues. There is more info on Phabricator and on MediaWiki.org. |
Top domestic destinations edit
| Rank | City | Passengers | Carriers |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |  Atlanta, Georgia Atlanta, Georgia | 681,000 | Delta, Southwest, Spirit |
| 2 |  Dallas/Fort Worth, Texas Dallas/Fort Worth, Texas | 385,000 | American, Spirit |
| 3 |  Houston–Intercontinental, Texas Houston–Intercontinental, Texas | 374,000 | Spirit, United |
| 4 |  Orlando, Florida Orlando, Florida | 292,000 | Frontier, Southwest, Spirit |
| 5 |  Denver, Colorado Denver, Colorado | 284,000 | Frontier, Southwest, United |
| 6 |  Charlotte, North Carolina Charlotte, North Carolina | 254,000 | American |
| 7 |  Dallas–Love, Texas Dallas–Love, Texas | 248,000 | Southwest |
| 8 |  Los Angeles, California Los Angeles, California | 238,000 | Breeze, Delta, Southwest, Spirit |
| 9 |  Houston–Hobby, Texas Houston–Hobby, Texas | 220,000 | Southwest |
| 10 |  Fort Lauderdale, Florida Fort Lauderdale, Florida | 216,000 | JetBlue, Southwest, Spirit |
edit
| Rank | Airline | Passengers | Share |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Southwest Airlines | 4,296,000 | 34.77% |
| 2 | Delta Air Lines | 2,061,000 | 16.68% |
| 3 | American Airlines | 1,703,000 | 13.78% |
| 4 | United Airlines | 1,564,000 | 12.65% |
| 5 | Spirit Airlines | 1,176,000 | 9.52% |
| Other | 1,557,000 | 12.60% |
Accidents and incidents edit
- On November 16, 1959 National Airlines Flight 967, a Douglas DC-7 flying from Tampa to New Orleans crashed into the Gulf of Mexico.[48] All 42 passengers and crew were killed.
- On February 25, 1964, Eastern Air Lines Flight 304 operated with a Douglas DC-8 flying from New Orleans International Airport to Washington Dulles International Airport crashed nine minutes after takeoff. All 51 passengers and 7 crew members were killed.[49]
- On March 30, 1967, Delta Air Lines Flight 9877, a Douglas DC-8-51, a training exercise with 6 crewmembers aboard, crashed on approach to MSY at 12:50 AM Central Time Zone after simulating a two-engine out approach, resulting in a loss of control. All 6 crewmembers and 13 on the ground were killed. The DC-8 crashed into a residential area, destroying several homes and a motel complex.[50]
- On March 20, 1969, Douglas DC-3 N142D, leased from Avion Airways for a private charter, crashed on landing, killing 16 of the 27 passengers and crew members on board. The aircraft was operating a domestic non-scheduled passenger flight from Memphis International Airport, Tennessee.[51]
- On July 9, 1982, Pan Am Flight 759, en route from Miami to San Diego, departed New Orleans International on its way to a second stop-over at Las Vegas. The Boeing 727-200 jetliner took off from the east–west runway (Runway 10/28) traveling east but never gained an altitude higher than 150 feet (46 m). The aircraft traveled 4,610 feet (1405 m) beyond the end of Runway 10, hitting trees along the way, until crashing into a residential neighborhood. A total of 153 people were killed (all 145 on board and 8 on the ground). The crash was, at the time, the second-deadliest civil aviation disaster in U.S. history. The National Transportation Safety Board (NTSB) determined the probable cause was the aircraft's encounter with a microburst-induced wind shear during the liftoff. This atmospheric condition created a downdraft and decreasing headwind forcing the plane downward. Modern wind shear detection equipment protecting flights from such conditions is now in place both onboard planes and at most commercial airports, including Armstrong International.[52]
- On May 24, 1988, TACA Flight 110 was forced to glide without power and make an emergency landing on top of a levee east of New Orleans International Airport after flame-out in both engines of the Boeing 737-300 in a severe thunderstorm. There were no casualties and the aircraft was subsequently repaired and returned to service.[53]
- On April 4, 2011, United Airlines Flight 497 en route from New Orleans to San Francisco made an emergency landing back at New Orleans after the flight crew reported smoke on board. The aircraft excursed from the runway during landing, sustaining minor damage. All 109 people on board evacuated the aircraft with no injuries. The NTSB determined that the captain had failed to properly manage the warning about smoke, which was actually erroneous and had been caused by contamination. No smoke was found on board the aircraft.[54]
See also edit
References edit
![]() This article incorporates public domain material from the Air Force Historical Research Agency
This article incorporates public domain material from the Air Force Historical Research Agency
External links edit

- Louis Armstrong New Orleans International Airport, official site
- Archive index at the Wayback Machine (hosted on Greater New Orleans Free Net, GNOFN, Inc.)
- FAA Airport Diagram for MSY (PDF), effective May 16, 2024
- FAA Terminal Procedures for MSY, effective May 16, 2024

