Inhibitors of dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP-4 inhibitors or gliptins) are a class of oral hypoglycemics that block the enzyme dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4). They can be used to treat diabetes mellitus type 2.
The first agent of the class – sitagliptin – was approved by the FDA in 2006.[1]
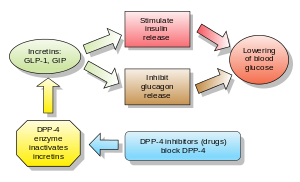
Glucagon increases blood glucose levels, and DPP-4 inhibitors reduce glucagon and blood glucose levels. The mechanism of DPP-4 inhibitors is to increase incretin levels (GLP-1 and GIP),[2][3][4] which inhibit glucagon release, which in turn increases insulin secretion, decreases gastric emptying, and decreases blood glucose levels.
A 2018 meta-analysis found no favorable effect of DPP-4 inhibitors on all-cause mortality, cardiovascular mortality, myocardial infarction or stroke in patients with type 2 diabetes.[5]
Examples
editDrugs belonging to this class are:
- Sitagliptin[6] (FDA approved 2006, marketed by Merck & Co. as Januvia)
- Vildagliptin[7] (EU approved 2007, marketed in the EU by Novartis as Galvus)
- Saxagliptin (FDA approved in 2009, marketed as Onglyza)
- Linagliptin (FDA approved in 2011, marketed as Tradjenta by Eli Lilly and Company and Boehringer Ingelheim)[8]
- Gemigliptin (approved in Korea in 2012, marketed by LG Life Sciences)[9] Marketed as Zemiglo
- Anagliptin (approved in Japan as Suiny in 2012, marketed by Sanwa Kagaku Kenkyusho Co., Ltd. and Kowa Company, Ltd.)[10]
- Teneligliptin (approved in Japan as Tenelia in 2012[11])
- Alogliptin (FDA approved 2013 as Nesina/ Vipidia, marketed by Takeda Pharmaceutical Company)
- Trelagliptin (approved for use in Japan as Zafatek/ Wedica in 2015)
- Omarigliptin (MK-3102) (approved as Marizev in Japan in 2015,[12] developed by Merck & Co.; research showed that omarigliptin can be used as once-weekly treatment and generally well tolerated throughout the base and extension studies[13])
- Evogliptin (approved as Suganon/ Evodine for use in South Korea[14])
- Gosogliptin (approved as Saterex for use in Russia[15])
- Dutogliptin (PHX- 1149 free base, being developed by Phenomix Corporation), Phase III[16]
- Neogliptin[17]
- Retagliptin (SP-2086), approved in China.
- Denagliptin
- Cofrogliptin (HSK- 7653, compound 2)
- Fotagliptin
- Prusogliptin
Other chemicals which may inhibit DPP-4 include:
Adverse effects
editIn those already taking sulphonylureas, there is an increased risk of low blood sugar when taking a medicine in the DPP-4 drug class.[19]
Adverse effects include nasopharyngitis, headache, nausea, heart failure, hypersensitivity and skin reactions.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is warning that the type 2 diabetes medicines like sitagliptin, saxagliptin, linagliptin, and alogliptin may cause joint pain that can be severe and disabling. FDA has added a new Warning and Precaution about this risk to the labels of all medicines in this drug class, called dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors.[20] However, studies assessing risk of rheumatoid arthritis among DPP-4 inhibitor users have been inconclusive.[21]
A 2014 review found increased risk of heart failure with saxagliptin and alogliptin, prompting the FDA in 2016 to add warnings to the relevant drug labels.[22]
A 2018 meta analysis showed that use of DPP-4 inhibitors was associated with a 58% increased risk of developing acute pancreatitis compared with placebo or no treatment.[23]
A 2018 observational study suggested an elevated risk of developing inflammatory bowel disease (specifically, ulcerative colitis), reaching a peak after three to four years of use and decreasing after more than four years of use.[24]
A 2020 Cochrane systematic review did not find enough evidence of reduction of all-cause mortality, serious adverse events, cardiovascular mortality, non-fatal myocardial infarction, non-fatal stroke or end-stage renal disease when comparing metformin monotherapy to dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors for the treatment of type 2 diabetes.[25]
Cancer
editIn response to a report of precancerous changes in the pancreases of rats and organ donors treated with the DPP-4 inhibitor sitagliptin,[26][27] the United States FDA and the European Medicines Agency each undertook independent reviews of all clinical and preclinical data related to the possible association of DPP-4 inhibitors with pancreatic cancer. In a joint letter to the New England Journal of Medicine, the agencies stated that they had not yet reached a final conclusion regarding a possible causative relationship.[28]
A 2014 meta-analysis found no evidence for increased pancreatic cancer risk in people treated with DPP-4 inhibitors, but owing to the modest amount of data available, was not able to completely exclude possible risk.[29]
Combination drugs
editSome DPP-4 inhibitor drugs have received approval from the FDA to be used with metformin concomitantly with additive effect to increase the level of glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) which also decreases hepatic glucose production.[citation needed]