This article needs additional citations for verification. (September 2018) |
The Province of Ontario has 51 first-level administrative divisions, which collectively cover the whole province. With two exceptions,[a] their areas match the 49 census divisions Statistics Canada has for Ontario.
| First-level administrative divisions of Ontario | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Location | Province of Ontario |
| Number | 51 |
| Populations | 13,255 (Manitoulin District) – 2,731,571 (City of Toronto) |
| Areas | 630.20 km2 (City of Toronto) – 407,268.65 km2 (Kenora District) |
The Province has four types of first-level division: single-tier municipalities, regional municipalities, counties, and districts. The first three are types of municipal government but districts are not—they are defined geographic areas (some quite large) used in many contexts. The last three have within them multiple smaller, lower-tier municipalities but the single-tier municipalities do not. Regional municipalities and counties differ primarily in the services that they provide to their residents. (Lower-tier municipalities are generally treated as census subdivisions by Statistics Canada.)
In some cases, an administrative division may retain its historical name even if it changes government type. For instance, Oxford County, Haldimand County, Norfolk County and Prince Edward County are no longer counties: Oxford is a regional municipality and the others are single-tier municipalities. Several administrative divisions in Ontario have significantly changed their borders or have been discontinued entirely. See: Historic counties of Ontario.
Types of administrative divisions
editSingle-tier municipalities
editThis section needs additional citations for verification. (September 2018) |
| Single-tier municipalities of Ontario | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Location | Province of Ontario |
| Number | 11[a] |
| Populations | 24,735 (Prince Edward County) – 2,731,571 (City of Toronto) |
| Areas | 630.20 km2 (City of Toronto) – 3,239.02km2 (City of Greater Sudbury) |
| Government | |
| Subdivisions |
|
A single-tier municipality is governed by one municipal administration, with neither a county nor regional government above it, nor further municipal subdivisions below it (cf. independent city).[1] Single-tier municipalities are either former regional municipalities or counties whose municipal governments were amalgamated in the 1990s into a single administration. Some single-tier municipalities of this type (e.g., Toronto, Ottawa, Hamilton, Greater Sudbury) were created where a former regional municipality consisted of a single dominant urban centre and its suburbs or satellite towns or villages, while others (e.g., Brant County, Chatham-Kent, Haldimand-Norfolk, Kawartha Lakes, and Prince Edward County) were created from predominantly rural divisions with a collection of distinct communities.
A single-tier municipality should not be confused with a separated municipality; such municipalities are considered as part of their surrounding county for census purposes, but are not administratively connected to the county.
With the exception of Greater Sudbury, single-tier municipalities that are not considered to be part of a county, regional municipality, or district are found only in Southern Ontario.
Current single-tier municipalities in Ontario that are also census divisions:
| Single-tier municipality | Population (2016)[2] | Area (km2) | Density (/km2) | Seat | Secondary region | Primary region |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Municipality of Chatham-Kent[b] | 102,042 | 2,457.90 | 41.4 | Chatham | Southwestern | Southern |
| City of Greater Sudbury[c] | 161,647 | 3,239.02 | 49.9 | Sudbury | Northeastern | Northern |
| Haldimand-Norfolk[a][d] | 109,787 | 2,894.76 | 37.9 | Cayuga, Simcoe | Southwestern | Southern |
| City of Hamilton[e] | 536,917 | 1,117.29 | 480.6 | Hamilton | Golden Horseshoe | Southern |
| City of Kawartha Lakes[f] | 75,423 | 3,084.38 | 24.5 | Lindsay | Central | Southern |
| City of Ottawa[g] | 934,243 | 2,790.30 | 334.8 | Ottawa | Eastern | Southern |
| Prince Edward County | 24,735 | 1,050.49 | 23.5 | Picton | Central | Southern |
| County of Brant[a] | 134,808 | 1,093.22 | 123.3 | Burford | Southwestern | Southern |
| City of Toronto[h] | 2,731,571 | 630.20 | 4,334.4 | Toronto | Golden Horseshoe | Southern |
Regional municipalities
editThis section needs additional citations for verification. (September 2018) |
| Regional municipalities of Ontario | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Location | Province of Ontario |
| Number | 8 |
| Populations | 60,599 (District Municipality of Muskoka) – 1,381,739 (Peel) |
| Areas | 964.05 km2 (Halton) – 3,940.48 km2 (District Municipality of Muskoka) |
| Government | |
| Subdivisions | |
Regional municipalities (or regions) are upper-tier municipalities that generally have more servicing responsibilities than the counties. They generally provide the following services: maintenance and construction of arterial roads in both rural and urban areas, transit, policing, sewer and water systems, waste disposal, region-wide land use planning and development, as well as health and social services. Regions are typically more urbanized than counties. Regional municipalities are typically an administrative division where an interconnected cluster of urban centres or suburbs forms the majority of the division's area and population, but no single centre is overwhelmingly dominant over the others. Regional municipalities are found only in Southern Ontario.
Although Oxford County and the District Municipality of Muskoka are not called regions, they are defined as regional municipalities under Part 1, Section 1 of the Ontario Municipal Act, 2001.[3]
Between 1998 and 2001, four regional municipalities that formed their own central city-dominated metropolitan areas were amalgamated and are now single-tier municipalities.
- In 1998, the Municipality of Metropolitan Toronto became the amalgamated City of Toronto.
- In 2001, the Regional Municipality of Ottawa–Carleton became the City of Ottawa, the Regional Municipality of Hamilton–Wentworth became the City of Hamilton, and the Regional Municipality of Sudbury became the City of Greater Sudbury. At the same time, the Regional Municipality of Haldimand–Norfolk was split into Haldimand County and Norfolk County.
Current regional municipalities in Ontario:
| Regional municipality | Population (2016)[2] | Area (km2) | Density (/km2) | Regional seat | Secondary region | Primary region |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Regional Municipality of Durham | 645,862 | 2,523.80 | 255.9 | Whitby | Golden Horseshoe | Southern |
| Regional Municipality of Halton | 548,435 | 964.05 | 568.9 | Oakville | Golden Horseshoe | Southern |
| District Municipality of Muskoka | 60,599 | 3,940.48 | 15.4 | Bracebridge | Northeastern | Northern |
| Regional Municipality of Niagara | 447,888 | 1,854.23 | 241.5 | Thorold | Golden Horseshoe | Southern |
| Oxford County | 110,862 | 2,039.61 | 54.4 | Woodstock | Southwestern | Southern |
| Regional Municipality of Peel | 1,381,739 | 1,246.95 | 1,108.1 | Brampton | Golden Horseshoe | Southern |
| Regional Municipality of Waterloo | 535,154 | 1,368.92 | 390.9 | Kitchener | Southwestern | Southern |
| Regional Municipality of York | 1,109,909 | 1,762.13 | 629.9 | Newmarket | Golden Horseshoe | Southern |
Counties
editThis section needs additional citations for verification. (September 2018) |
| Counties of Ontario | |
|---|---|
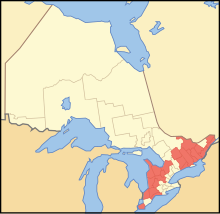 | |
| Location | Province of Ontario |
| Number | 22 |
| Populations | 18,062 (Haliburton) – 479,650 (Simcoe) |
| Areas | 1,486.44 km2 (Dufferin) – 7,448.57 km2 (Renfrew) |
| Government | |
| Subdivisions | |
Counties have fewer responsibilities than regions, as the lower-tier municipalities (cities, towns, villages, townships) within the counties typically provide the majority of municipal services to their residents. The responsibilities of county governments are generally limited to the following: maintenance and construction of rural arterial roads, health and social services, and county land use planning. Counties are only found in Southern Ontario and are also mostly census divisions.
Counties may be as large as regional municipalities in population, but their population density is generally lower (although not as low as in a district.) Counties may include major cities, such as London, Kingston and Windsor, geographically located within them, but these communities are usually separated municipalities that are only considered part of the county for census purposes, but are not administratively connected to the county. Municipalities are separated when regional or single-tier status is not appropriate for the municipality's population patterns, but their population is still large enough that it may adversely affect the county's ability to provide services to its smaller communities. Also, these cities have not evolved into large urban agglomerations with other communities, as in regions and single-tier cities, but may have small suburbs such as Point Edward.
Current counties in Ontario:
| County | Population (2016)[2] | Area (km2) | Density (/km2) | County seat | Secondary region | Primary region |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bruce County | 68,147 | 4,090.20 | 16.7 | Walkerton | Southwestern | Southern |
| Dufferin County | 61,735 | 1,486.44 | 41.5 | Orangeville | Central | Southern |
| Elgin County | 88,978 | 1,881.03 | 47.3 | St. Thomas | Southwestern | Southern |
| Essex County | 398,953 | 1,850.90 | 215.5 | Essex | Southwestern | Southern |
| Frontenac County | 150,475 | 3,787.76 | 39.7 | Kingston | Eastern | Southern |
| Grey County | 93,830 | 4,513.50 | 20.8 | Owen Sound | Southwestern | Southern |
| Haliburton County | 18,062 | 4,076.08 | 4.4 | Minden | Central | Southern |
| Hastings County | 136,445 | 6,103.92 | 22.4 | Belleville | Central | Southern |
| Huron County | 59,297 | 3,399.27 | 17.4 | Goderich | Southwestern | Southern |
| Lambton County | 126,638 | 3,002.25 | 42.2 | Wyoming | Southwestern | Southern |
| Lanark County | 68,698 | 3,035.64 | 22.6 | Perth | Eastern | Southern |
| United Counties of Leeds and Grenville | 100,546 | 3,382.89 | 29.7 | Brockville | Eastern | Southern |
| Lennox and Addington County | 42,888 | 2,839.68 | 15.1 | Napanee | Eastern | Southern |
| Middlesex County | 455,526 | 3,317.27 | 137.3 | London | Southwestern | Southern |
| Northumberland County | 85,598 | 1,905.15 | 44.9 | Cobourg | Central | Southern |
| Perth County | 76,796 | 2,218.52 | 34.6 | Stratford | Southwestern | Southern |
| Peterborough County | 138,236 | 3,848.20 | 35.9 | Peterborough | Central | Southern |
| United Counties of Prescott and Russell | 89,333 | 2,004.47 | 44.6 | L'Orignal | Eastern | Southern |
| Renfrew County | 102,394 | 7,448.57 | 13.7 | Pembroke | Eastern | Southern |
| Simcoe County | 479,650 | 4,859.64 | 98.7 | Midhurst | Central | Southern |
| United Counties of Stormont, Dundas and Glengarry | 113,429 | 3,309.87 | 34.3 | Cornwall | Eastern | Southern |
| Wellington County | 222,726 | 2,660.57 | 83.7 | Guelph | Southwestern | Southern |
Districts
editThis section needs additional citations for verification. (September 2018) |
| Districts of Ontario | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Location | Province of Ontario |
| Number | 10 |
| Populations | 13,255 (Manitoulin) – 146,048 (Thunder Bay) |
| Areas | 3,107.23 km2 (Manitoulin) – 407,268.65 km2 (Kenora) |
| Government |
|
Districts are regional areas in Northern Ontario that do not serve any municipal government purpose. Although districts do still contain incorporated cities, towns and townships, they do not have an upper-tier county or regional municipality level of government, and are largely composed of unorganized areas. Some districts may have District Social Service Administration Boards, which are designed to provide certain social services, but they do not serve a governmental function.
In a district, all services are provided either by the municipalities themselves, by local services boards in some communities within the unorganized areas, or directly by the provincial government. Much of Northern Ontario is sparsely populated, so a county government structure would not be an efficient or cost-effective method of administration.
The former Regional Municipality of Sudbury, created in 1973, was the only division in Northern Ontario ever incorporated with a structure like those of counties, regional municipalities, and single-tier municipalities in the southern part of the province. That division was dissolved in 2000, and now constitutes the single-tier municipality of Greater Sudbury.
Current districts in Ontario:
| District | Population (2016)[2] | Area (km2) | Density (/km2) | District seat | Secondary region | Primary region |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Algoma District | 114,094 | 48,814.88 | 2.3 | Sault Ste. Marie | Northeastern | Northern |
| Cochrane District | 79,682 | 141,268.51 | 0.6 | Cochrane | Northeastern | Northern |
| Kenora District | 65,533 | 407,268.65 | 0.2 | Kenora | Northwestern | Northern |
| Manitoulin District | 13,255 | 3,107.23 | 4.3 | Gore Bay | Northeastern | Northern |
| Nipissing District | 83,150 | 17,103.78 | 4.9 | North Bay | Northeastern | Northern |
| Parry Sound District | 42,824 | 9,326.48 | 4.6 | Parry Sound | Northeastern | Northern |
| Rainy River District | 20,110 | 15,486.75 | 1.3 | Fort Frances | Northwestern | Northern |
| Sudbury District | 21,546 | 40,204.77 | 0.5 | Espanola | Northeastern | Northern |
| Thunder Bay District | 146,048 | 103,722.82 | 1.4 | Thunder Bay | Northwestern | Northern |
| Timiskaming District | 32,251 | 13,303.30 | 2.4 | Haileybury | Northeastern | Northern |
See also
editNotes
edit- ^ a b c d Statistics Canada treats Norfolk County and Haldimand County as one single census division; the County of Brant and City of Brantford are also treated as one single census division. There would otherwise be 51 census divisions instead of the 49 official ones used by Statistics Canada.
- ^ Formerly Kent County
- ^ Formerly Regional Municipality of Sudbury
- ^ Formerly the Regional Municipality of Haldimand-Norfolk
- ^ Formerly the Hamilton-Wentworth Regional Municipality
- ^ Formerly Victoria County
- ^ Formerly the Regional Municipality of Ottawa-Carleton
- ^ Formerly Metropolitan Toronto
References
edit- ^ "List of Ontario municipalities". Government of Ontario. Retrieved 14 August 2020.
- ^ a b c d "Population and dwelling counts, for Canada, provinces and territories, and census divisions, 2016 and 2011 censuses". Statistics Canada. Retrieved 2017-02-08.
- ^ Ontario Municipal Act, 2001.
External links
edit